1947-1948 Palestine War. Image source: Business Insider Australia (Kelley 2013)
By: Yvonne Wu, Sofia Ranieri, Nabeeha Ahsan
The following is the first of a series of three articles covering the history behind the crisis in Palestine. This article covers events from the 19th century until the 1947–1949 Palestine war.
In the late 19th century, Palestine was ruled by the Ottoman Empire, and briefly by Egypt. Under the empire, people of different religions lived peacefully together. Meanwhile, Europe was experiencing a rapid rise in nationalism, prompting Theodor Herzl, a Jewish journalist, to advocate for an ideology and nationalist movement called Zionism (CrashCourse 2015).
In 1917, the British government issued the Balfour Declaration, “establishing Palestine as a national home for Jewish people,” in a time when Palestine was still part of the Ottoman Empire. A year earlier, Britain divided Arab territories with France, with British keeping Palestine. To further complicate this, in 1915 the British promised Sharif Hussein, the ruler of Mecca, that he would rule over an Arab state, including Palestine, if he revolted against Ottoman rule, which he did. Over the span of three years, the British promised Palestine to Meccans, themselves, and Zionists (CrashCourse 2015).

James Balfour and the Balfour Declaration. Image source: My Jewish Learning (Shumel 2017)

Arab Palestinians revolting against the British, 1936. Image source: A News Education (Hilbert 2021)
After World War I (1914-1918), the British took control of Palestine and divided Christians, Jews, and Muslims into separate institutions. Due to easier immigration facilitated by the British, the Jewish population increased by 320,000, making up just under 30% of the population at the time. Many purchased land from absentee non-Palestinian Arab landowners, then evicting Palestinian farmers who were living and working on the land. The reasoning behind this was to control both land and labour to create a more secure community within Palestine, but instead, it increased tensions between Jewish People and Arab Palestinians.
In the years leading up to 1936, there was a growing sense of Palestinian nationalism. This culminated with the 1936-1939 Palestinian revolt against the British, which was the first sustained violent uprising of Palestinian Arabs in more than a century. There were calls for strikes, bans, and closing of local governments by Arab political parties. Jewish settlements and British installations were attacked by Arab rebels, and the movement had grown to be a national revolt. The British army responded by backing Jewish militias, which did little to subdue arson, bombings, and assassinations. A 1937 investigation run by Lord Robert Peel, called the Peel Commission recommended that the land be partitioned, giving the Jewish state a partition of land much larger than the existing Jewish land owned (Encyclopedia Britannica 2021). The Arabs were opposed to this and to the suggestion that they would be forcibly transferred, which increased the strength of the revolt during 1937-1938.
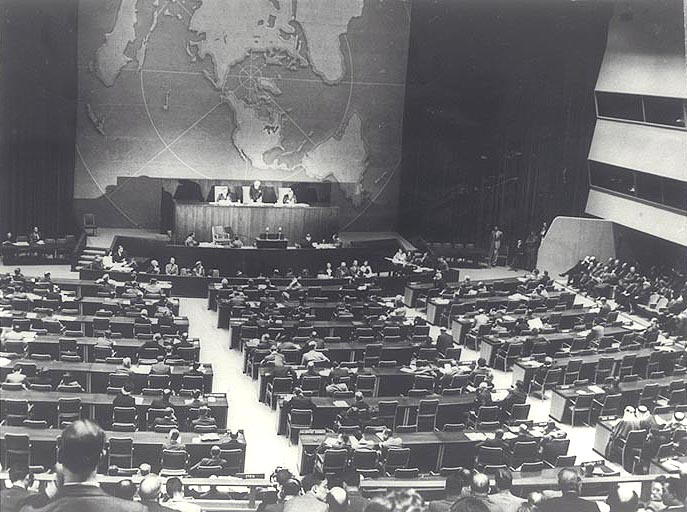

United Nations meeting about the Partition of Palestine, November 29, 1947. Image source: SpecialOperations.com (Balestrieri 2017)
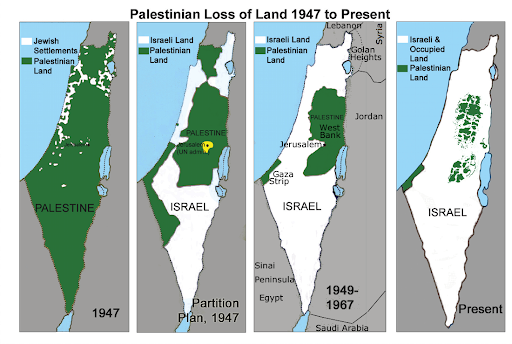
After World War II (1939-1945), the British assigned the crisis of Palestine to the newly formed United Nations. In 1947, Palestine was divided into two sections, an independent Jewish state and an independent Arab state. Jerusalem, on the other hand, was to be an international territory with a special status because it was claimed as a capital for the Arabs and the Jews. Many Palestinian Arabs did not agree with this decision due to the fact that they have been fighting against the Jewish and British in Palestine since the 1920s. Arab groups demanded more territory, because they had a larger population, and began to create volunteer armies around Palestine. After Britain withdrew from Palestine in 1948, Israel became an independent state, which Arab armies attempted to prevent (Encyclopedia Britannica 2021). This sparked a war between Israel and Jordan, Iraq, Syria, Egypt, and Lebanon. When the Arab-Israeli war ended in 1949, Israel controlled over two thirds of the land allotted by the Balfour Declaration, Jordan controlled the West Bank, and Egypt controlled the Gaza Strip. This war also led about 700 thousand Pakistanis to flee their homes and become refugees.
Definitions
Zionism - the national movement for the return of the Jewish people to their homeland and the renewal of Jewish freedom in Israel (Jewish Virtual Library n.d.)
Balfour Declaration - A letter written by British Foregin Secretary Arthur Balfour where he expressed the British government’s support for Zionism (History.com Editors 2017)
Mecca - holy city in western Saudi Arabia (Merriam-Webster 2021)
United Nations - An international organization where all the world’s nations can gather together, discuss common problems, and find shared solutions (U.N. n.d.)
Jordan - a country in Southwest Asia (WorldAtlas 2021)
Egypt - a country in Africa (WorldAtlas 2021)
Additional Timeline
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1FuRXs3jNJK-Alx4omUOsuqtdIhZsYx59/view
Works Cited
“About Us.” United Nations, United Nations, www.un.org/en/about-us.
Balestrieri, Steve. “November 29, 1947, the U.N. Partition Plan for Palestine Is Adopted.” SpecialOperations.com, 29 Nov. 2017, specialoperations.com/32058/november-29-1947-u-n-partition-plan-palestine-adopted/.
CrashCourse. “Conflict in Israel and Palestine: Crash Course World History 223.” YouTube, YouTube, 28 Jan. 2015, www.youtube.com/watch?v=1wo2TLlMhiw.
Encyclopedia Britannica. “The Arab Revolt.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 2021, www.britannica.com/place/Palestine/The-Arab-Revolt.
Ettinger, Shmuel. “The Balfour Declaration of 1917.” My Jewish Learning, 18 Oct. 2017, www.myjewishlearning.com/article/the-balfour-declaration/.
Hilbert, Anna. “Guide: Britain and the Israel-Palestine Conflict.” A News Education, A News Education, 4 Jan. 2021, www.anewseducation.com/post/britain-and-the-israel-palestine-conflict.
History.com Editors. “Balfour Declaration.” History.com, A&E Television Networks, 14 Dec. 2017, www.history.com/topics/middle-east/balfour-declaration.
History.com Editors. “Palestine.” History.com, A&E Television Networks, 11 Aug. 2017, www.history.com/topics/middle-east/palestine.
Kelley, Michael. “Stunning Pictures From The Early Days Of Israel.” Business Insider Australia, Business Insider Australia, 15 May 2013, www.businessinsider.com.au/stunning-pictures-from-the-early-days-of-israel-2013-5#in-1917-during-world-war-i-zionist-volunteers-assisted-britains-conquest-of-palestine-jewish-immigration-to-the-area-increased-thereafter-1.
McBride, Don. Arab Israeli Wars, 2016, donsnotes.com/hist/arab-israeli-wars.html.
“Mecca.” Merriam-Webster, Merriam-Webster, 2021, www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/mecca.
WorldAtlas. “Egypt Maps & Facts.” WorldAtlas, WorldAtlas, 24 Feb. 2021, www.worldatlas.com/maps/egypt.
WorldAtlas. “Jordan Maps & Facts.” WorldAtlas, WorldAtlas, 24 Feb. 2021, www.worldatlas.com/maps/jordan.
“Zionism.” A Definition of Zionism, Jewish Virtual Library, www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/a-definition-of-zionism.