Image of the Six Day War
https://www.jta.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/6-day.jpg
By: Sofia Ranieri
The following is the second of a series of three articles covering the history behind the crisis in Palestine. This first article covers events from the 19th century until the 1947–1949 Palestine war. This article covers events between 1967 to 2014.
The Six Day War began April 1967 when clashes between Israel and Syria escalated to an air and military exchange. In the initial conflict, six Syrian fighter jets were destroyed. After this battle, the Soviets falsely informed Egypt that Israel was moving its soldiers to the northern border with Syria to prepare for a full scale invasion, and due to this intelligence, the Egyptian President moved troops to that area. A United Nations peacekeeping force had to step in to ensure no violence ensued. On June 5, 1967, a preemptive aerial attack on Egypt was launched from Israel. Israel constantly fought its neighbouring countries over the course of six days. By the end of this, Israel seized the Gaza Strip, the Sinai Peninsula, and Golan Heights, as well as the West Bank and Arab sector of East Jerusalem, and by end of this, Israel land had doubled in size.
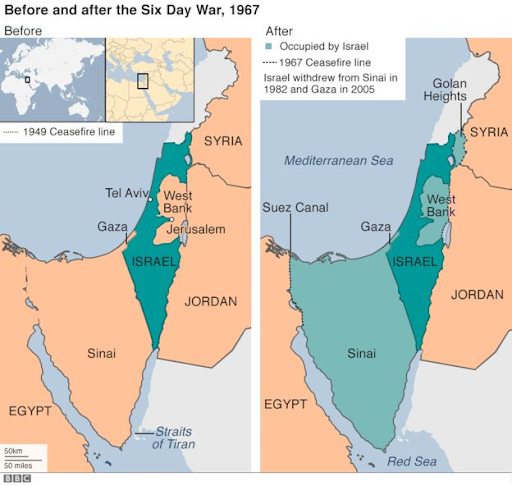
Israel’s territory before and after the Six Day War
After rejecting the call of withdrawal from the UN Security Council, Israel indicated that the territories they conquered would be returned if Arabs acknowledged the right for Israel to exist and was ensured against future attack. Arab leaders decided that there would be no peace, negotiations, or recognition of Israel and intended to defend the rights of Palestinian Arabs in the occupied territories. After this battle the conflict between Israel and its neighbors would continue with the First Intifada in 1987. The word “Intifada” translates to “shaking off” in Arabic, and was used to describe the Palestinian riots. The Palestinian militia groups revolted, and as a consequence hundreds of people were killed. Later on, in the early 1990s, the Oslo Peace Accords were introduced as an effort to end the violence. The first of the Oslo Accords, signed in 1993, initiated a timetable for a Middle East peace process and a plan for an acting Palestinian government in areas of Gaza and the West Bank. The second Oslo Accord introduced a complete removal of Israeli troops from areas in the West Bank and other occupied areas. It also included a plan for Palestinian Legislative Council Elections. Ultimately, the Oslo Peace Accords failed because Israel and Palestine could not agree over a peace plan. The second Intifada began in September 2000, when Ariel Sharon, a Jewish Israeli, later Prime Minister of Israel, went to the holy site for Muslims - the Al-Aqsa mosque. Suicide bombings, riots and other attacks lasted for about 5 years, over one thousand Israelis were killed and trauma from this event is still evident today. Finally, in August 2005, the Israeli troops left Gaza, the Prime Minister of Israel claimed that this was to “reduce terror as much as possible, and grant Israeli citizens the maximum level of security” (Stead).

Image from the Second Intifada
Although the Israeli troops withdrew, there was still a limited amount of peace in Palestine in the following years. In 2006, fighting between Hamas and Fatah began after Hamas won the Palestinian legislative elections and kidnapped a member of Fatah. In a fight for Gaza, Hamas became very violent against Fatah. The clashes ended when Palestinian Authority Chairman Mahmound Abbas, Palestinian Prime Minister Ismali Haniyeh, as well as other leaders called for peace. Hamas has also participated in suicide bombings and has called for the destruction of Israel several times, which caused other countries to view this group as a terrorist organisation. Other conflicts ensued such as Operation Cast Lead in December 2008, and Operation Pillar Defense in November 2012. These operations caused Hamas and Fatah to decide on an agreement which formed a unified national Palestinian government in April 2014, merging the groups against Israel.
There are still conflicts in this area today, with the recent crisis in Palestine. There has been lots of negative history between Palestine and Israel; the countries almost never get along. Conflicts such as the Six Day War, the First and Second Intifada, as well as the operations listed above occur often in this region. For more information on Palestine, read the previous article about the history of this country from the 1900s to 1967. The final article of this series will be about the crisis in Palestine during 2021 and will be coming soon!
Definitions
Palestinian Legislative Council Elections - Elections to determine who will be part of the Palestine Legislative Council. This council was created to represent Palestinians living in Gaza, the West Bank, East Jerusalem, etc.
Hamas - Militant Palestinian nationalist and Islamist in the West Bank and the Gaza Strip that is dedicated to the establishment of an independant Islamic state is historical Palestine. (“The Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica'')
Fatah - A Palestinian terrorist organization with the goal of destroying the state of Israel
Operation Cast Lead - A disagreement between the Palestinians in the Gaza Strip and Israel. Israel claimed that their aim was to stop indiscriminate Palestinian rocket fire into Israel and weapons smuggling into the Gaza Strip. (“Operation Cast Lead: Background & Overview”)
Operation Pillar Defense - The Israel Defense Forces began this due to an escalation in rocket fire by terrorists in Gaza
Works Cited
Crashcourse. YouTube, YouTube, 28 Jan. 2015, www.youtube.com/watch?v=1wo2TLlMhiw.
“Fatah.” The Free Dictionary, Farlex, www.thefreedictionary.com/Fatah.
“Hamas.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., www.britannica.com/topic/Hamas.
History.com Editors. “Palestine.” History.com, A&E Television Networks, 11 Aug. 2017, www.history.com/topics/middle-east/palestine.
“Intifada Begins on Gaza Strip.” History.com, A&E Television Networks, 9 Feb. 2010, www.history.com/this-day-in-history/intifada-begins-on-gaza-strip.
“Operation Cast Lead: Background & Overview.” Background & Overview of Operation Cast Lead, www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/background-and-overview-of-operation-cast-lead.
“Operation Pillar of Defense: Background & Overview.” Background & Overview of Operation Pillar of Defense, www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/background-and-overview-of-operation-pillar-of-defense.
“Six-Day War Begins.” History.com, A&E Television Networks, 9 Feb. 2010, www.history.com/this-day-in-history/six-day-war-begins.
Avi Issacharoff Haaretz Service, Agencies. “Two Killed and 18 Hurt in FRESH Hamas-Fatah Fighting in Gaza.” Haaretz.com, Haaretz, 30 Sept. 2006, www.haaretz.com/1.4871683.
“Palestinian Legislative Council (PLC) – Mapping Palestinian Politics.” ECFR, 20 Mar. 2018, ecfr.eu/special/mapping_palestinian_politics/palestine_legislative_council/.
“Remembering Israel's 'DISENGAGEMENT' from Gaza.” Middle East Monitor, 15 Aug. 2019, www.middleeastmonitor.com/20190815-remembering-israels-disengagement-from-gaza/.
“Report: Hamas, FATAH Agree to END Factional Fighting.” CNN, Cable News Network, www.cnn.com/2006/WORLD/meast/05/09/hamas.fatah/index.html.
“The Second Intifada: A Defining Event That Reshaped the Nation.” The Jerusalem Post | JPost.com, www.jpost.com/arab-israeli-conflict/the-second-intifada-a-defining-event-that-reshaped-the-nation-642644.